Mechanisms underlying pathogenesis of SARS-CoV‑2 infections
Yannick Stahl – Hector Fellow Ralf Bartenschlager
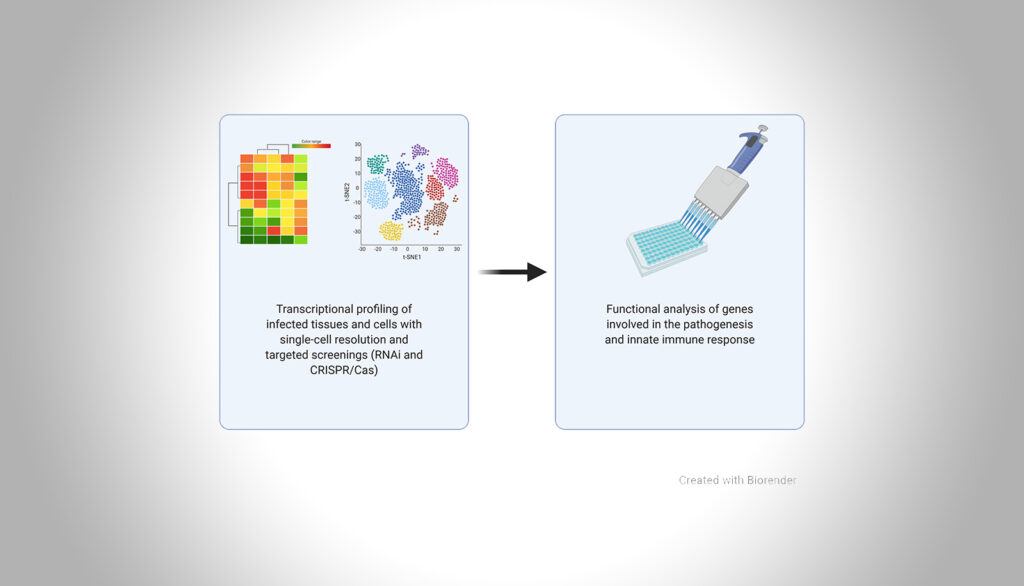
SARS-CoV‑2 has caused a pandemic and is responsible for more than 18 million infections. It is hypothesized that COVID-19 is the result of killing of infected cells and excessive immune activation. To reveal cell types and pathways that are critically involved in viral replication and pathogenesis, I will use transcriptomics and functional studies of genes likely involved in these processes. The results might inform the development of therapeutic strategies and the discovery of biomarkers.