Networking and interdisciplinary knowledge transfer
Alumni projectsCompleted projects
The Hector Fellow Academy has created a dynamic network for its alumni in order to maintain the dialogue between outstanding scientists beyond the project period. The regular exchange and transfer of research results as well as the opportunity for long-term interdisciplinary cooperation makes the HFA a vital academy of science. We are pleased that the following projects have been successfully completed.

Completed interdisciplinary projects
Fundamentals of gold catalysis
Dr. Sarah Bay – Hector Fellow A. Stephen K. Hashmi
Dr. Jean-Francois Greisch – Hector Fellow Manfred Kappes
In this project the characteristics of innovative gold catalysts are explored.
Mechanical Metamaterials
Dr. Claudio Findeisen – Hector Fellow Peter Gumbsch
Dr. Muamer Kadic – Hector Fellow Martin Wegener
In this project the characteristics of new metamaterials are investigated.
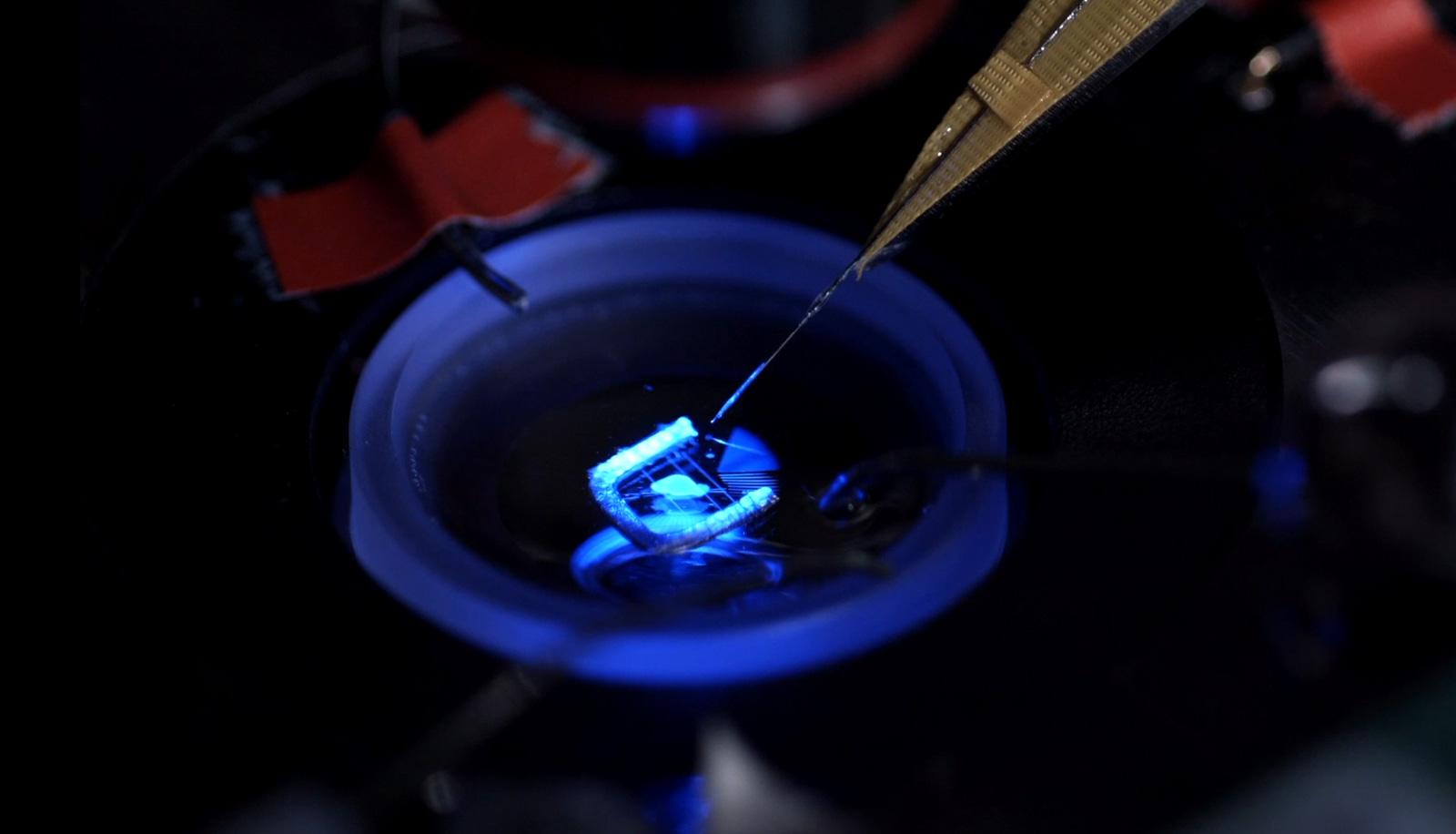
CarboChip: High performance micro-electrodes for retinal implants
Dr. Wadood Haq – Hector Fellow Eberhart Zrenner
Dr. Franz Selzer – Hector Fellow Karl Leo
Hector Fellow Manfred Kappes
Hector Fellow Martin Wegener
In this project new micro electrodes for retinal implants are being developed.
Stress & Epigenetics: Epigenetic effects of parental stress in offspring
Dr. Amber Makowicz — Hector Fellow Axel Meyer
In this project epigenetic modifications of gene expression by environmental stressors are investigated.
Towards Understanding the Genetic Basis of Appetitive Aggressive Behavior
Jan Gerwin – Hector Fellow Axel Meyer
Aggressive behavior can be of two distinct origins: (1) reactive aggression, as a response to threatening or dangerous situations and (2) appetitive aggression, that is motivated by intrinsic factors, for example positive feelings through the exertion of violence.
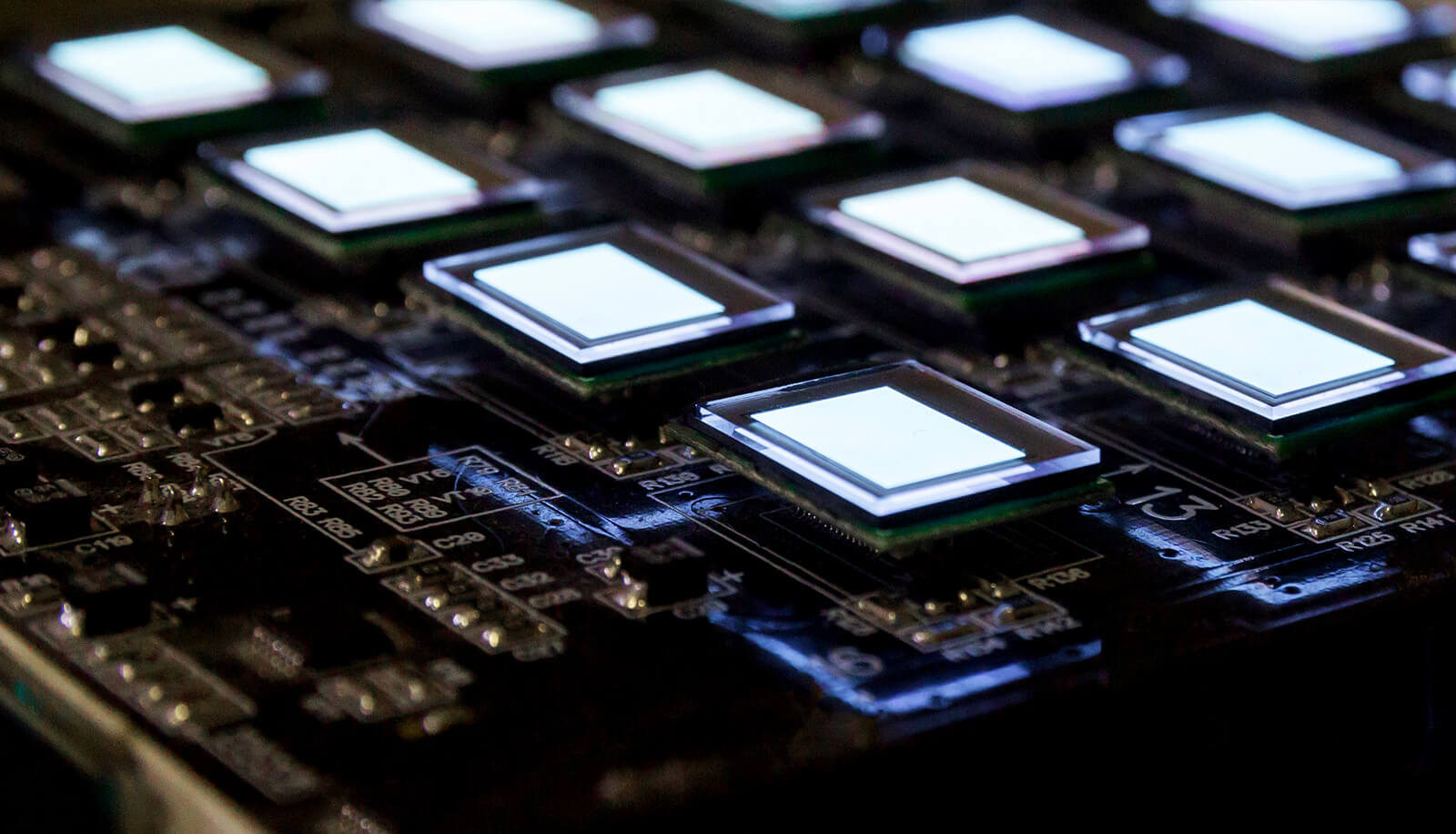
High-resolution optogenetics with organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs)
Giuseppe Ciccone – Hector Fellow Karl Leo
Rodrigo Fernandez Lahore – Hector Fellow Peter Hegemann
In this project, the application of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) in optogenetics will be investigated. Several new technological approaches will be addressed to achieve optogenetic activation and inhibition of neurons with previously impossible lateral resolution. For this purpose, a new OLED technology is to be used, which can imitate electrically switchable different colours.
Completed doctoral projects
Defining novel resilience pathways in rare monogenic disorders
Daniel Petersheim — Hector Fellow Christoph Klein
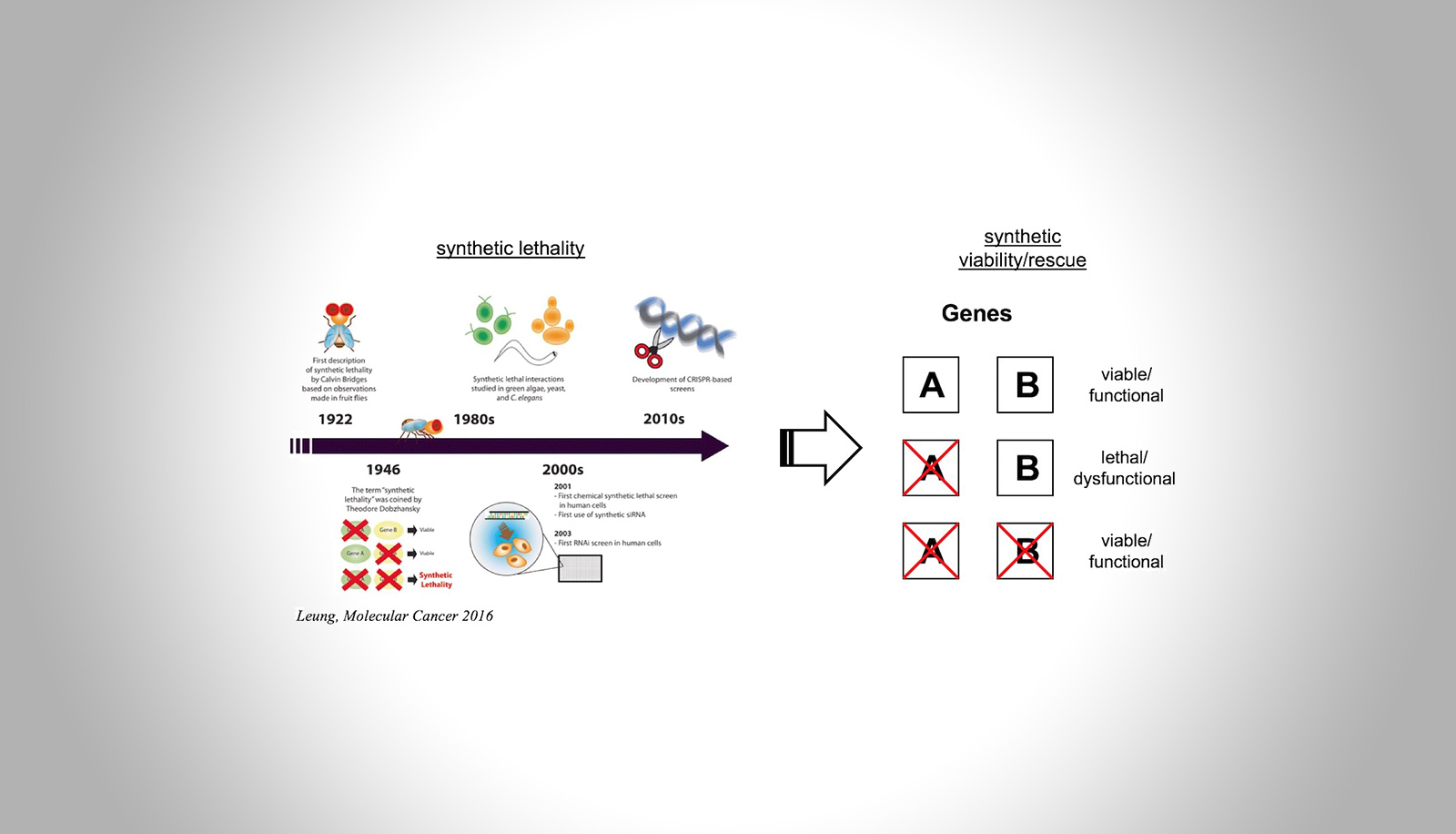
In the EU alone, approximately 30 million people are affected by a rare disease, many of them children. Most of the 6,000 to 8,000 rare diseases known to date are caused by the altered function of a single gene (Boycott&Ardigó, 2018). This project under the supervision of Prof. Christoph Klein aims to develop innovative strategies for precision medicine in rare diseases by (i) re-wiring aberrant molecular networks for therapeutic purposes and (ii) identifying novel “druggable” targets using CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome-wide screens.
High-throughput Virus Discovery in Next Generation Sequencing Data
Franziska Klingler – Hector Fellow Ralf Bartenschlager
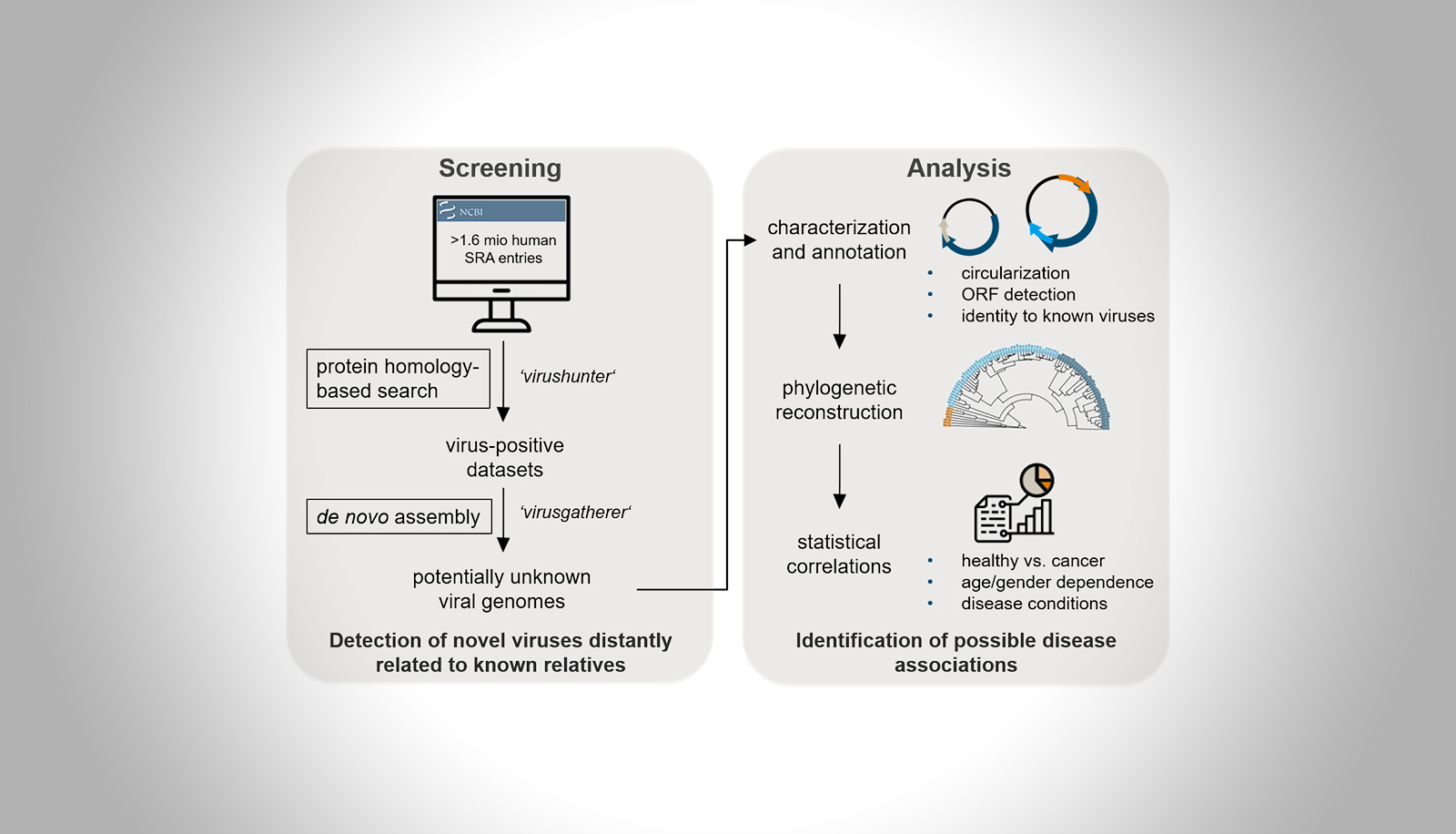
Anelloviruses are a diverse group of ubiquitous viruses infecting humans and vertebrates. Their contribution to disease development remains elusive. We hypothesize that during lifelong, persistent infection disbalances in the viral community can drive onset and progression of disease, e.g. cancer. We aim at a thorough description of the viral spectrum present in healthy and diseased tissue by high-throughput screening of sequencing data and subsequent identification of viral variants correlated with pathogenesis.
Machine learning methods for gravitational-wave data analysis
Maximilian Dax – Hector Fellow Bernhard Schölkopf
The detection of gravitational waves (GWs) has opened a new window on the universe, through which we can study the physics of black-hole and neutron-star mergers. By analyzing GWs we can infer properties of the corresponding astrophysical systems. Current analysis methods are however too computationally expensive to deal with the growing amount of data. My research is thus concerned with the development of more efficient methods for the GW analysis using powerful machine learning methods.
Quantum simulation of strong interactions of light and matter
Valentin Klüsener – Hector Fellow Immanuel Bloch
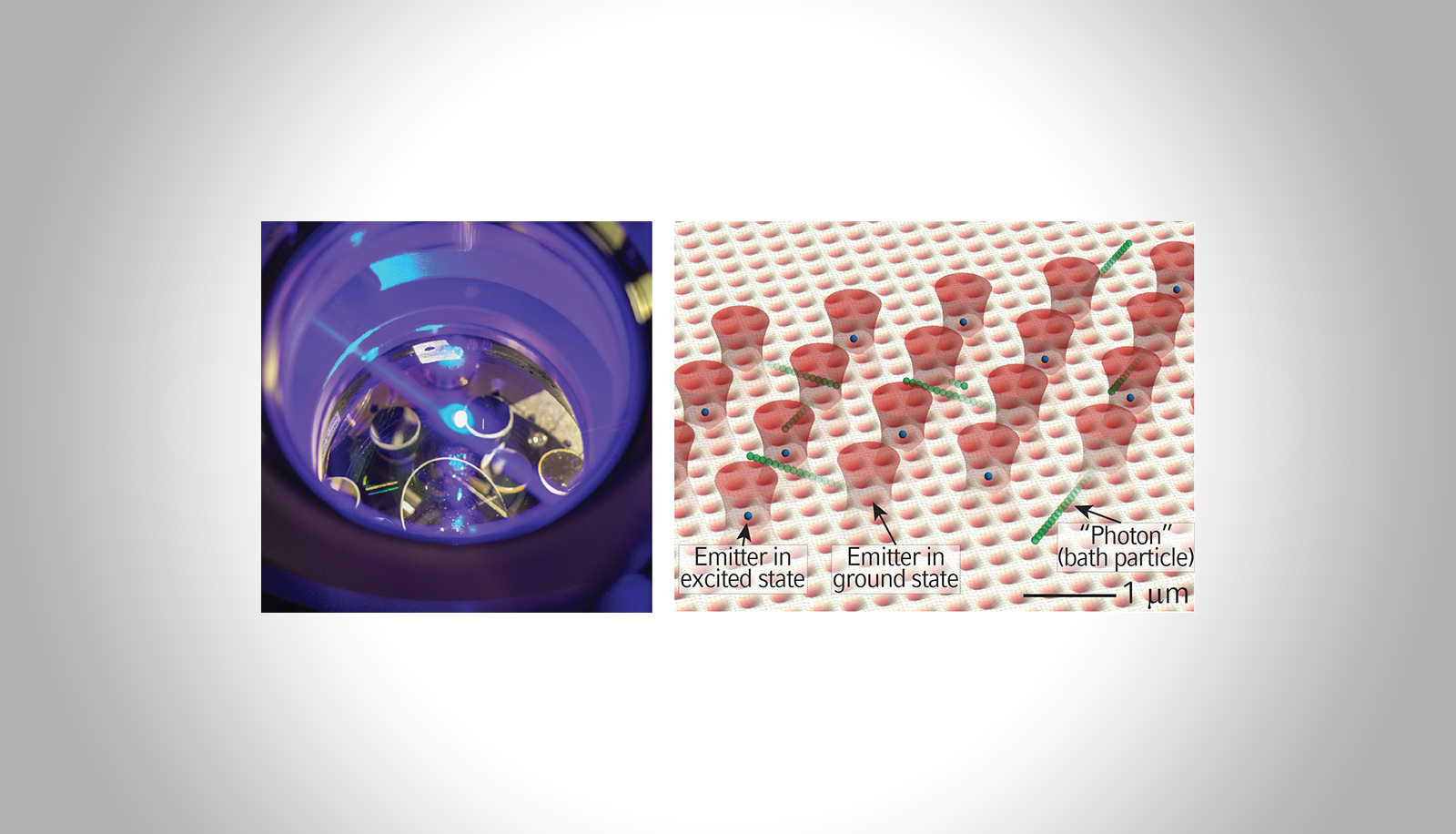
The central paradigm of quantum optics is the absorption and emission of radiation by quantum emitters. When the coupling between an emitter and its environment becomes strong, intriguing radiative properties can be engineered, such as directional emission patterns or strongly modified emission rates. This project aims at accessing such effects in a system of ultracold atoms in optical lattices where artificial emitters decay by emitting matter waves rather than optical radiation.
Mechanisms underlying pathogenesis of SARS-CoV‑2 infections
Yannick Stahl – Hector Fellow Ralf Bartenschlager
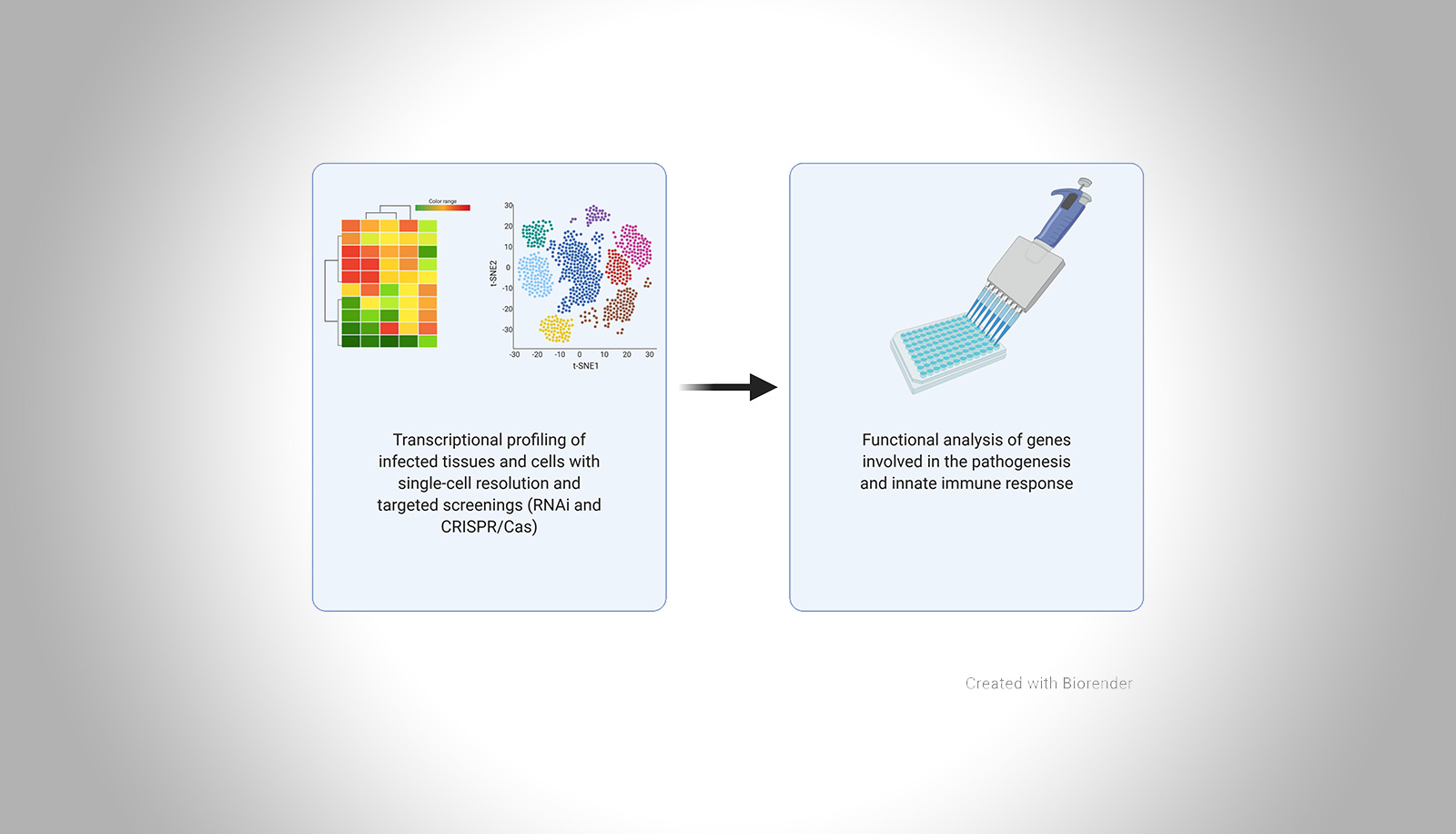
SARS-CoV‑2 has caused a pandemic and is responsible for more than 18 million infections. It is hypothesized that COVID-19 is the result of killing of infected cells and excessive immune activation. To reveal cell types and pathways that are critically involved in viral replication and pathogenesis, I will use transcriptomics and functional studies of genes likely involved in these processes. The results might inform the development of therapeutic strategies and the discovery of biomarkers.
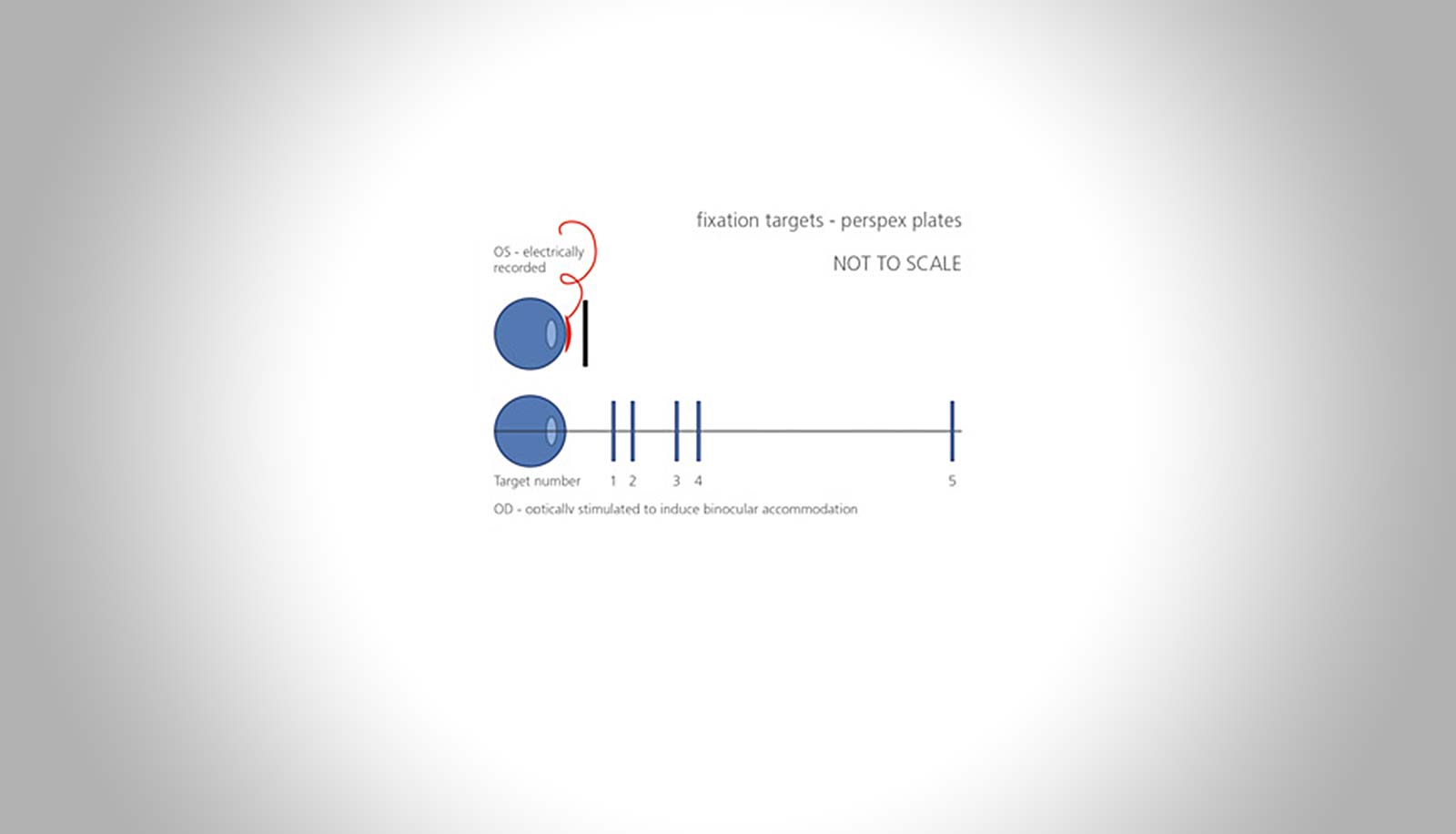
Applications of Non-Invasive Ocular Signal Measurements
Margaret Deibel – Hector Fellow Eberhart Zrenner
Several goals were pursued in the development of this work, including the development of a novel in vivo method to measure the ciliary muscle of a human subject non-invasively during accommodation, the characterization of the recorded muscle signals based on the accommodative abilities of the subject, and the development of a device that would utilize the recorded muscle signals to mimic the appropriate level of accommodation for the user, actuated through the use of a variable refractive lens.
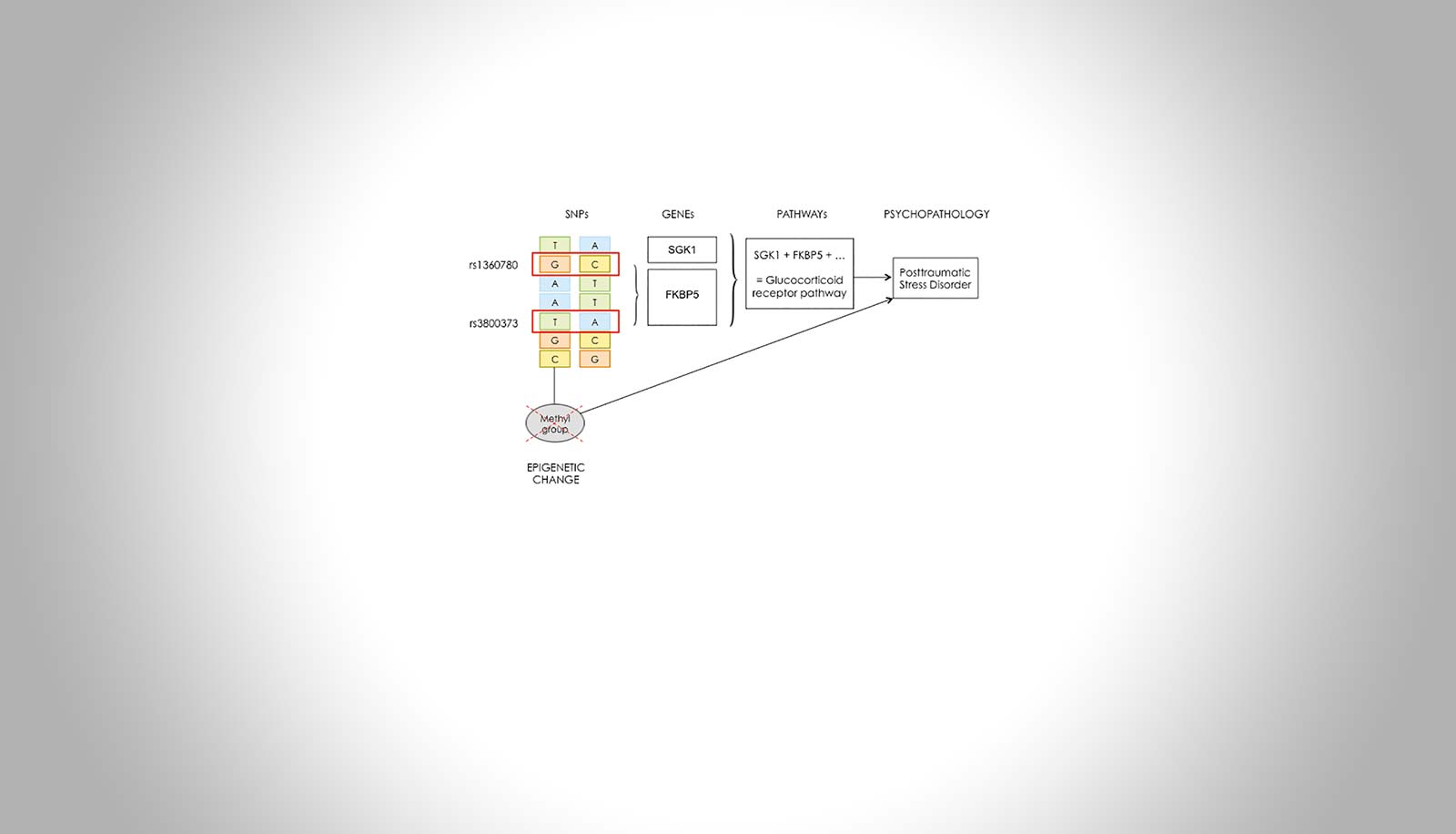
Genetics and Epigenetics of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and its Treatment
Daniela Conrad – Hector Fellow Thomas Elbert
The risk to develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) depends on the number of traumatic events experienced and individual risk factors, e.g. genetic predispositions. However, to identify causal genetic variants of this polygenic disease, trauma exposure needs to be adequately assessed.
Photocatalysis and Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Reactions of Furane-Derivatives
Daniel Eppel – Hector Fellow A. Stephen K. Hashmi
Fossil resources are increasingly depleted. They have to be replaced as quickly as possible by renewable raw materials, so that a slow transition to a new and modern production of „platform chemicals“ can take place.
Continuum Damage Models for Reliability Assessment of Structural Composites
Zalikha Murni Abdul Hamid – Hector Fellow Peter Gumbsch
The market’s demand for carbon fiber/epoxy composite has dramatically increased due to its significant applications and advantages in industry. Typical loading on the structures that are made up by this material often involves tensile and lateral bending of the composite laminates.
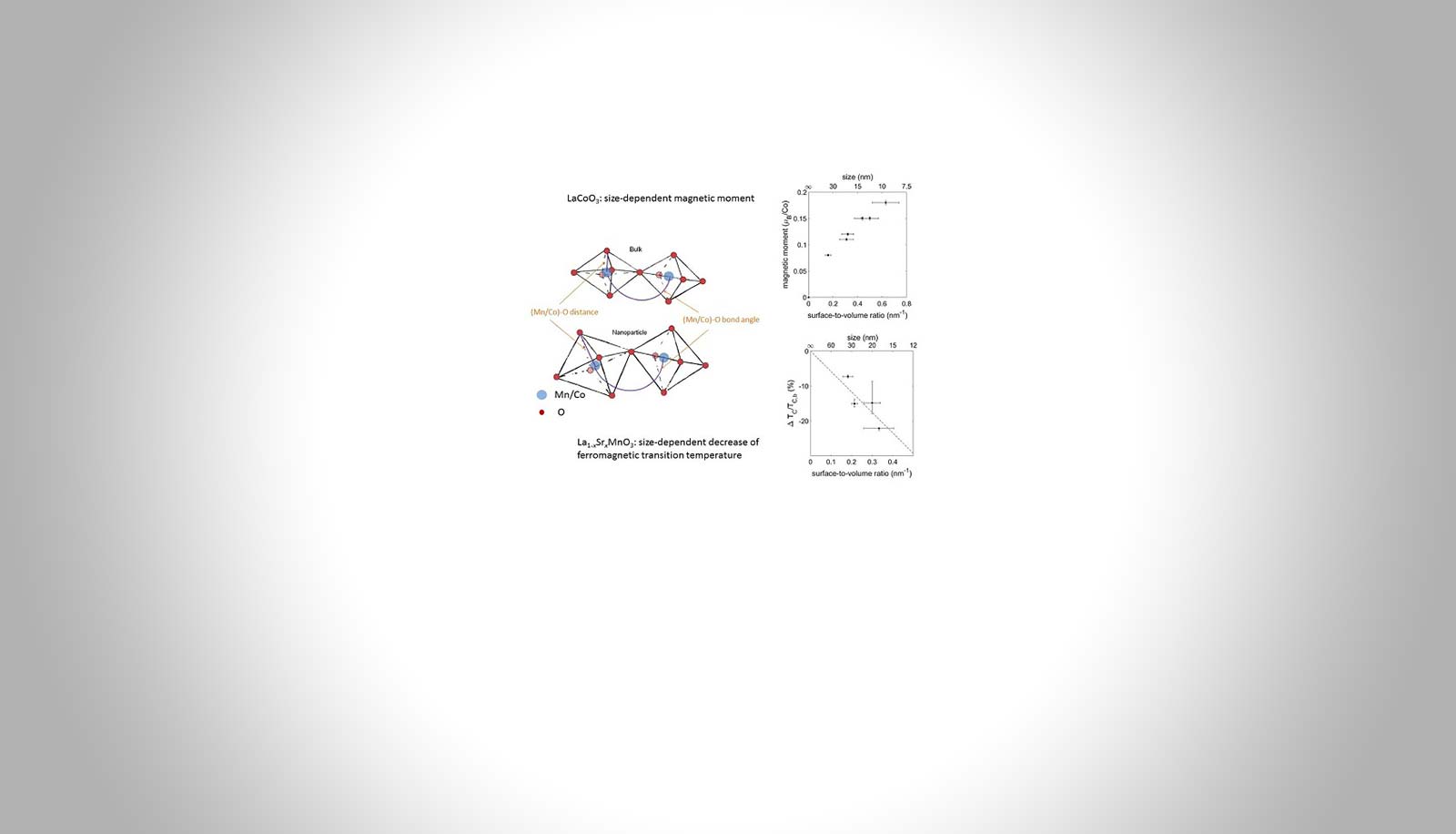
Magnetism in Perovskite Manganites and Cobaltites at the Nano Scale
Cornelia E. Hintze – Hector Fellow Hilbert von Löhneysen
The exact position of atoms in the crystal structure of lanthanum manganites and cobaltates (both anorganic ionic compounds) significantly affects their magnetic properties. The crystal structure of these materials can be altered by pressure, substitution of elements, or crystallite size: Since nanoparticles have a large surface-to-volume ratio, their surface has a dominant effect on the crystal structure, leading to changes compared to bulk materials.
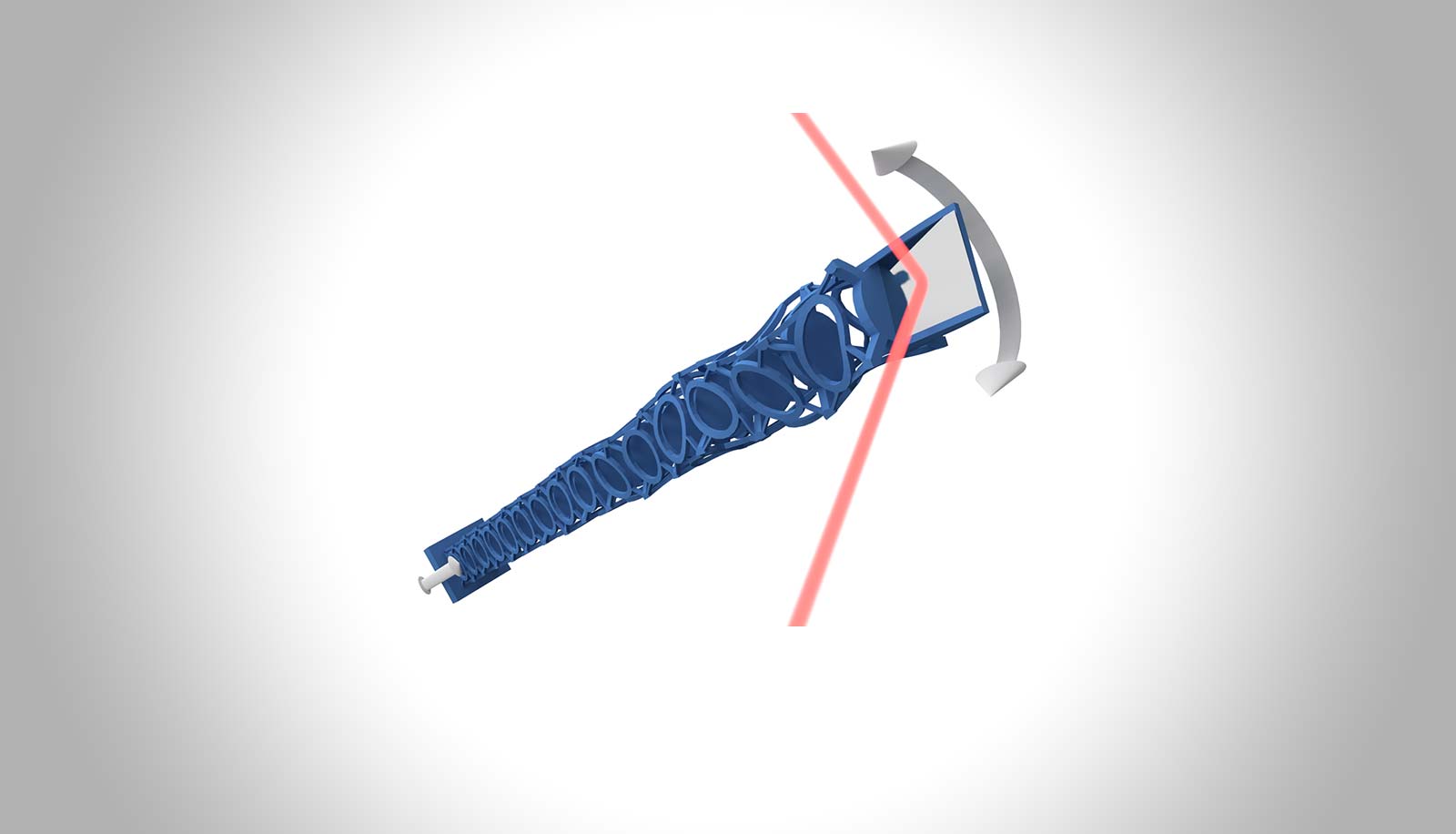
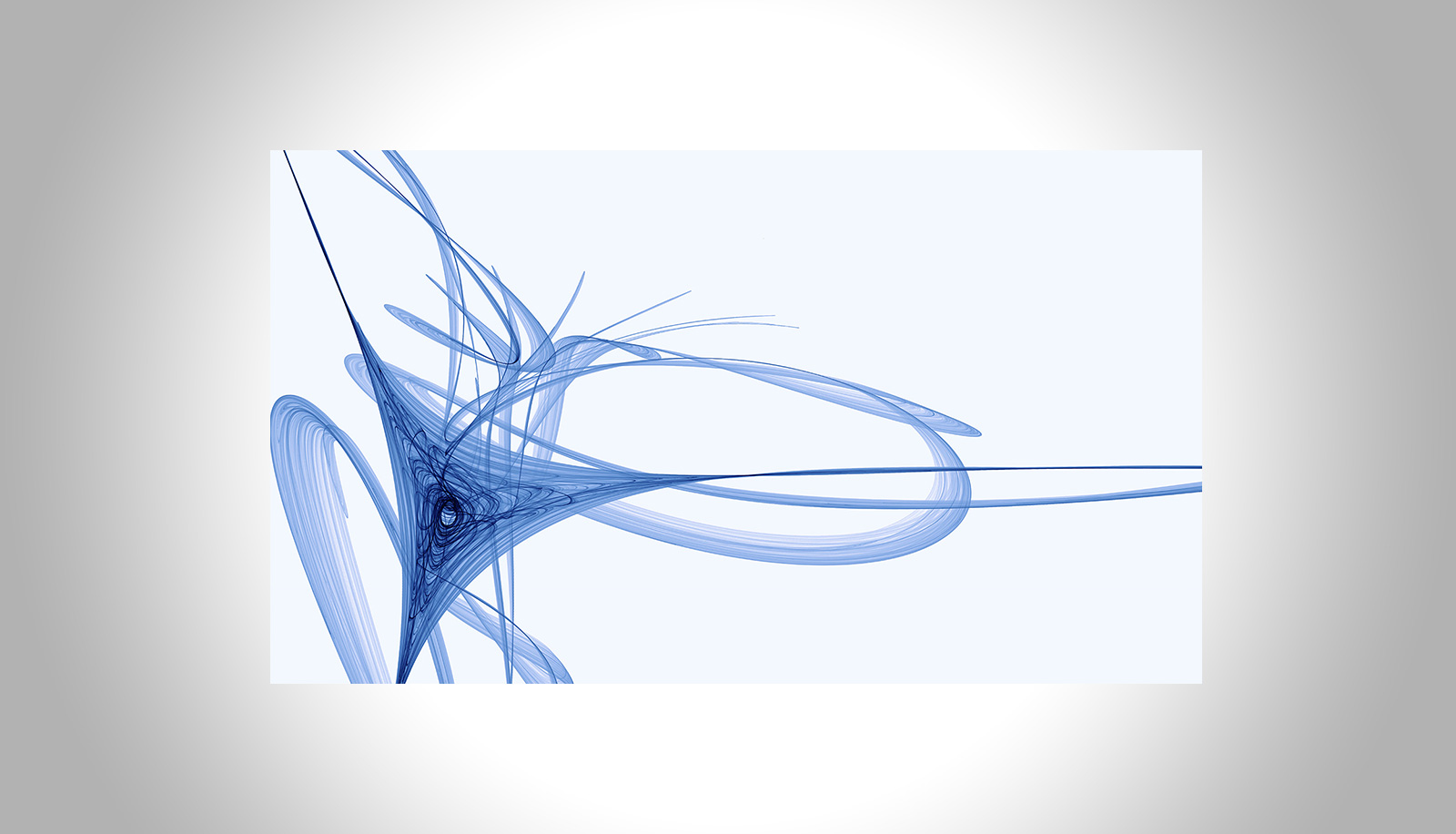
Three-dimensional Chiral Metamaterials
Julian Köpfler – Hector Fellow Martin Wegener
Metamaterials are rationally designed structures exhibiting effective macroscopic material properties that go beyond those of ordinary materials. For instance, by introducing so-called topologically protected resonances it is possible to locally enhance mechanical vibrations and make them robust against perturbations. In this project, chiral metamaterials with topologically protected resonances are designed and fabricated to realize a resonant mechanical laser-beam scanner (see Figure). Such laser-beam scanners are crucial for various applications such as LIDAR, confocal microscopy, projector displays, and material processing.
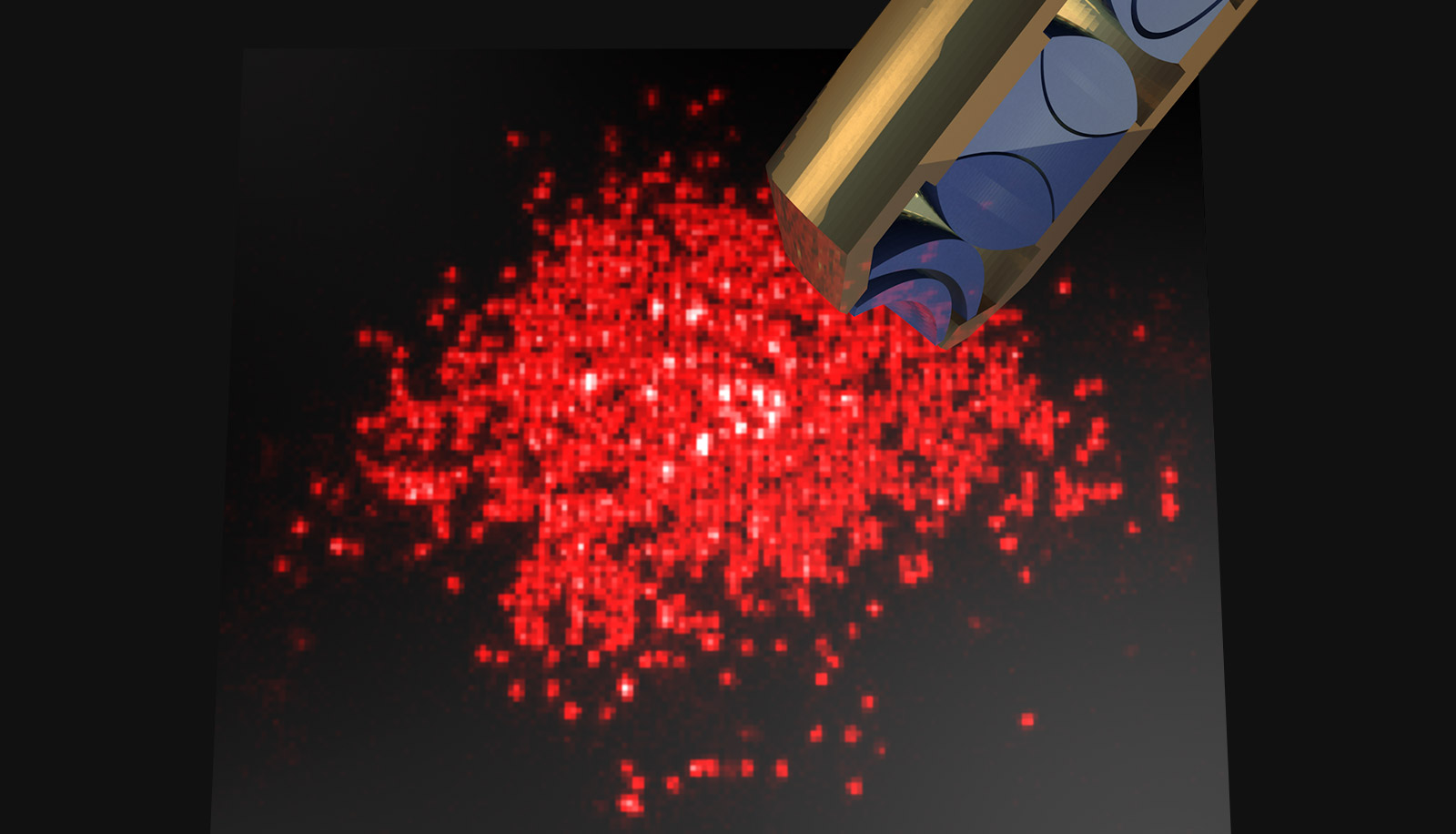
Fermionic Quantum Gas Microscope
Joannis Koepsell – Hector Fellow Immanuel Bloch
A rich variety of phenomena in solid state systems such as quantum magnetism or high temperature superconductivity still pose open questions on parts of their microscopic explanation. Due to the complexity of these systems, the underlying quantum many-body dynamics is often not accessible to computational simulation.
Completed Associated Young Researchers Projects
Modular Synthesis of Nitrogen-Stabilized Carbene Complexes
Vanessa Vethake — Hector Fellow A. Stephen K. Hashmi
This project dealt with the development of a modular synthesis that allows access to a wide range of catalysts with properties tailored to the needs of the reactions to be catalyzed. The synthesis makes it possible to construct various N‑heteroacyclic and N‑heterocyclic carbene ligands with a wide range of electronic and steric properties directly at the metal center.
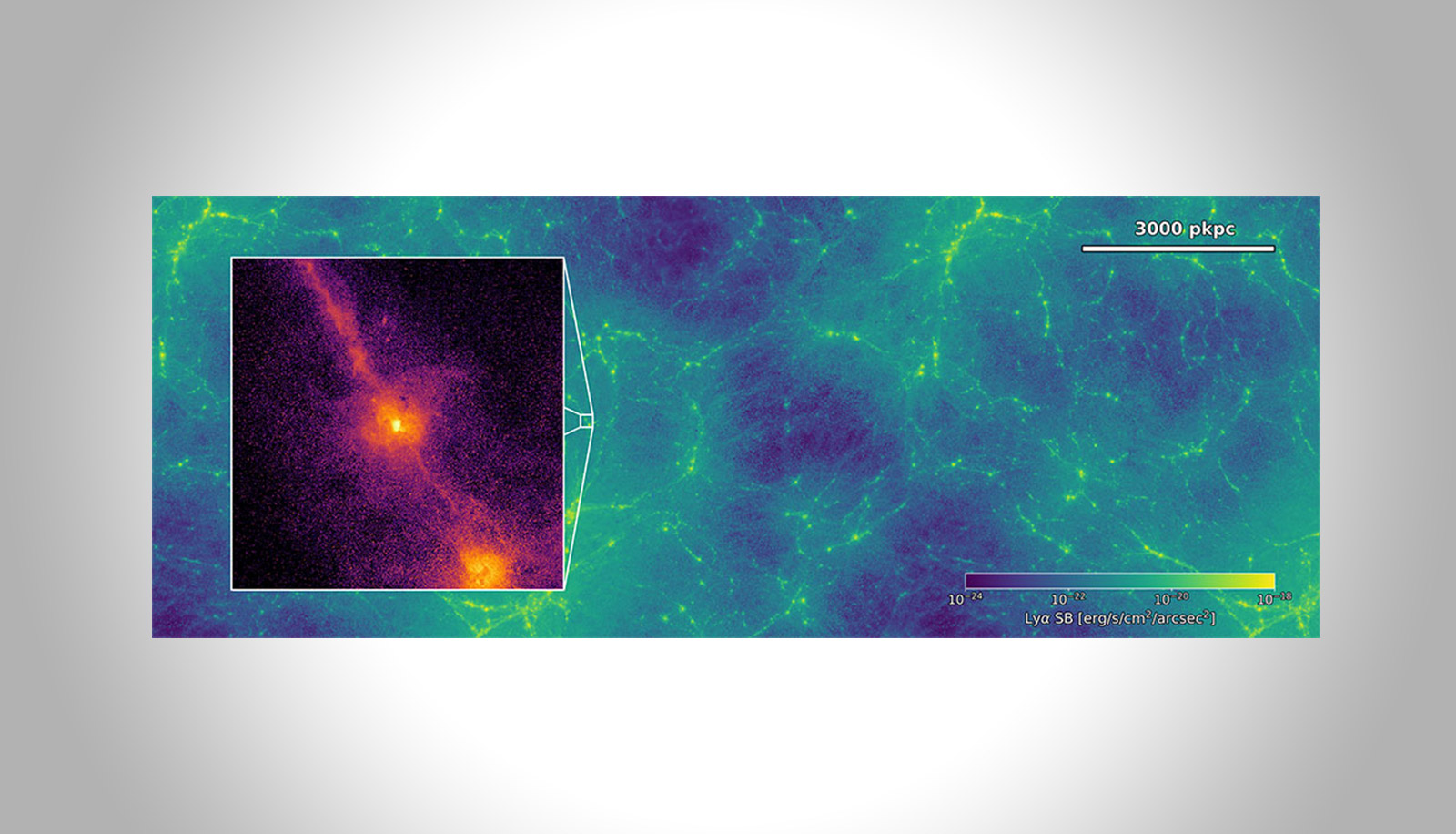
Circumgalactic medium and the cosmic web
Chris Byrohl — Hector RCD Awardee Dylan Nelson
A cosmic web of galaxies and diffuse gas permeates our Universe. This cosmic web glows through faint, but measurable, Lyman-alpha emission of its neutral hydrogen. This project aims to characterize said cosmic web in cosmological simulations of galaxy formation. Connecting to upcoming observational data sets, new pathways for our understanding of galaxy and structure formation emerge.
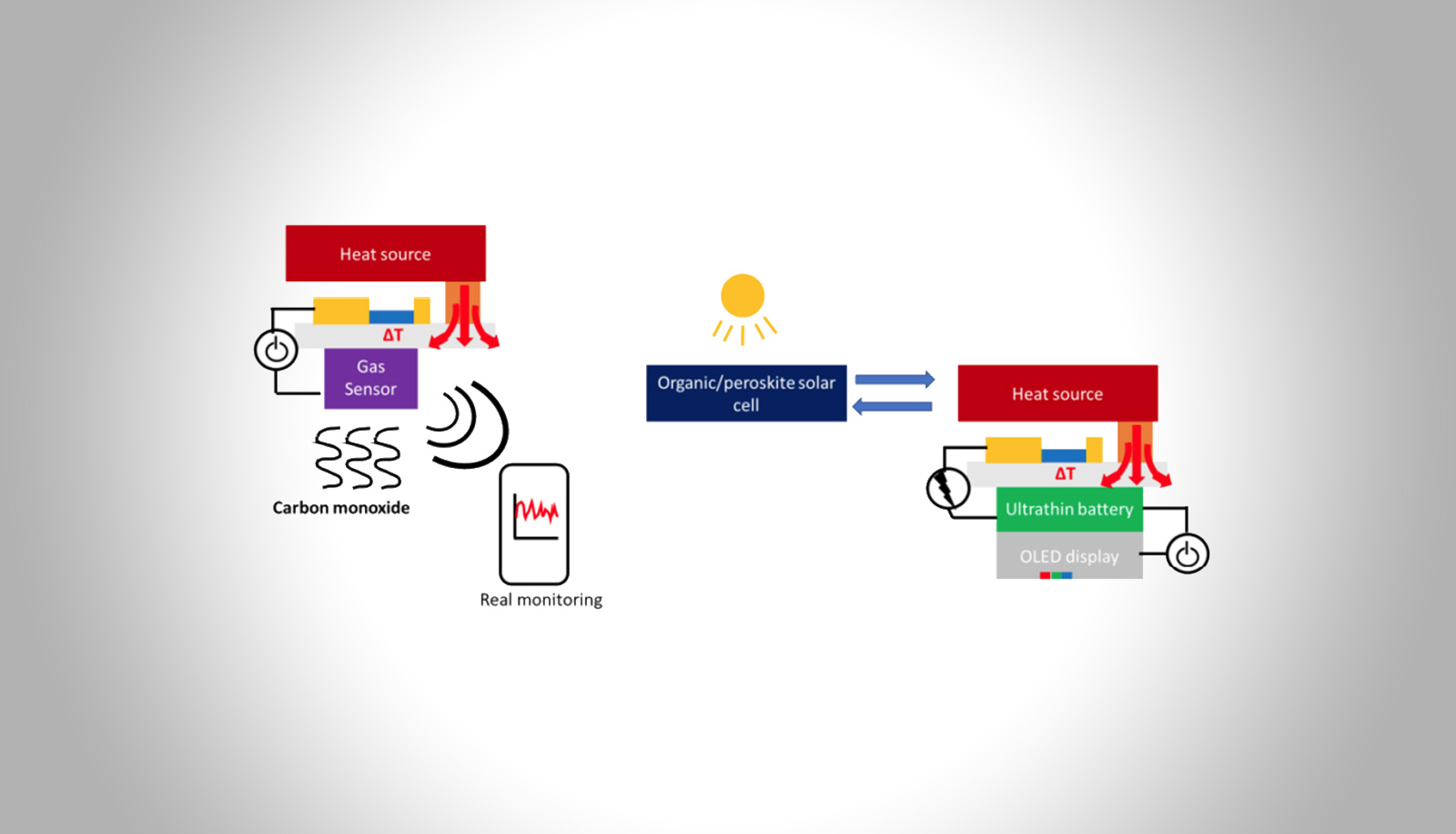
Novel applications with organic thermoelectric modules
Shu-Jen Wang – Hector Fellow Karl Leo
This project aims at using modulation doped organic thermoelectric modules for energy harvesting in niche areas where module flexibility is key. We will develop novel device architectures based on modulation doped organic thermoelectrics to enable innovative applications.